Marengo
Marengo is an embedding model for comprehensive video understanding. The current version is Marengo 3.0.
Marengo analyzes multiple modalities in video content, including visuals, audio, and text, to provide a holistic understanding similar to human comprehension.
Available versions
Deprecation notice
Marengo 2.7 will be deprecated after TwelveLabs automatically reindexes your videos to Marengo 3.0. Starting mid-March 2026, reindexing will roll out progressively. Review your integration now. See the Migration guide for details.
Key features
Marengo offers different capabilities depending on the version you use. Review the features below to understand what each version provides.
New in Marengo 3.0
Marengo 3.0 introduces the following new features:
- Composed text and image search: Combine text descriptions with images in a single search query for more precise results.
- Improved cinematography understanding: Enhanced search performance for cinematography terms like zoom, pan, and tracking shot.
- Sports intelligence: Improved recognition of soccer and basketball actions. Support for baseball, ice hockey, and American football.
- Faster indexing: Significant performance improvement with the new indexing technology.
- Extended text processing: Maximum text length increased from 77 to 500 tokens for both search queries and text embeddings.
- Optimized embeddings: 512-dimensional embeddings for faster processing and reduced storage.
- Long content support: Process up to four hours of video and audio content while maintaining context.
- Expanded language support: Query videos in 36 languages plus English (up from 12 plus English).
Standard features
The following features are available in all versions:
- Multimodal processing: Combines visual, audio, and text elements for comprehensive understanding.
- Fine-grained search: Detects brand logos, text, and small objects (as small as 10% of the video frame).
- Motion search: Identifies and analyzes movement within videos.
- Counting capabilities: Accurately counts objects in video frames.
- Audio comprehension: Analyzes music, lyrics, sound, and silence.
- Multilingual support: Query videos in 12 languages, in addition to English.
Use cases
- Search: Use text, images, video clips, or audio to find specific content. The model supports any-to-any search across multiple modalities.
- Embeddings: Create video embeddings for various downstream applications.
Input requirements
The table below summarizes the key differences between versions. For detailed specifications, see the sections that follow.
Image requirements are identical across both versions.
The specifications on this page reflect the maximum capabilities of the model. Your actual requirements depend on the upload method and operation you choose. For details about the available upload methods and the corresponding limits, see the Upload and processing methods page.
Video file requirements
Requirements vary depending on the version of the model:
Audio and video stream durations must not differ by more than 0.5 seconds.
For videos in other formats or if you require different options, contact us at support@twelvelabs.io.
Note
If you upload files using publicly accessible URLs, use direct links to raw video files that play without user interaction or custom video players (example: https://example.com/videos/sample-video.mp4). Video hosting platforms like YouTube and cloud storage sharing links are not supported.
Image file requirements
Use image files that meet these requirements:
Audio file requirements
Requirements vary depending on the version of the model:
Text input requirements
The maximum length varies depending on the model version and applies to both search queries and text embeddings.
Supported languages
Language support varies by model version. You can query videos in multiple languages, and language support applies to your queries, regardless of the language used in the content.
Examples
The examples in this section are from the Playground. However, the principles demonstrated are similar when invoking the API programmatically.
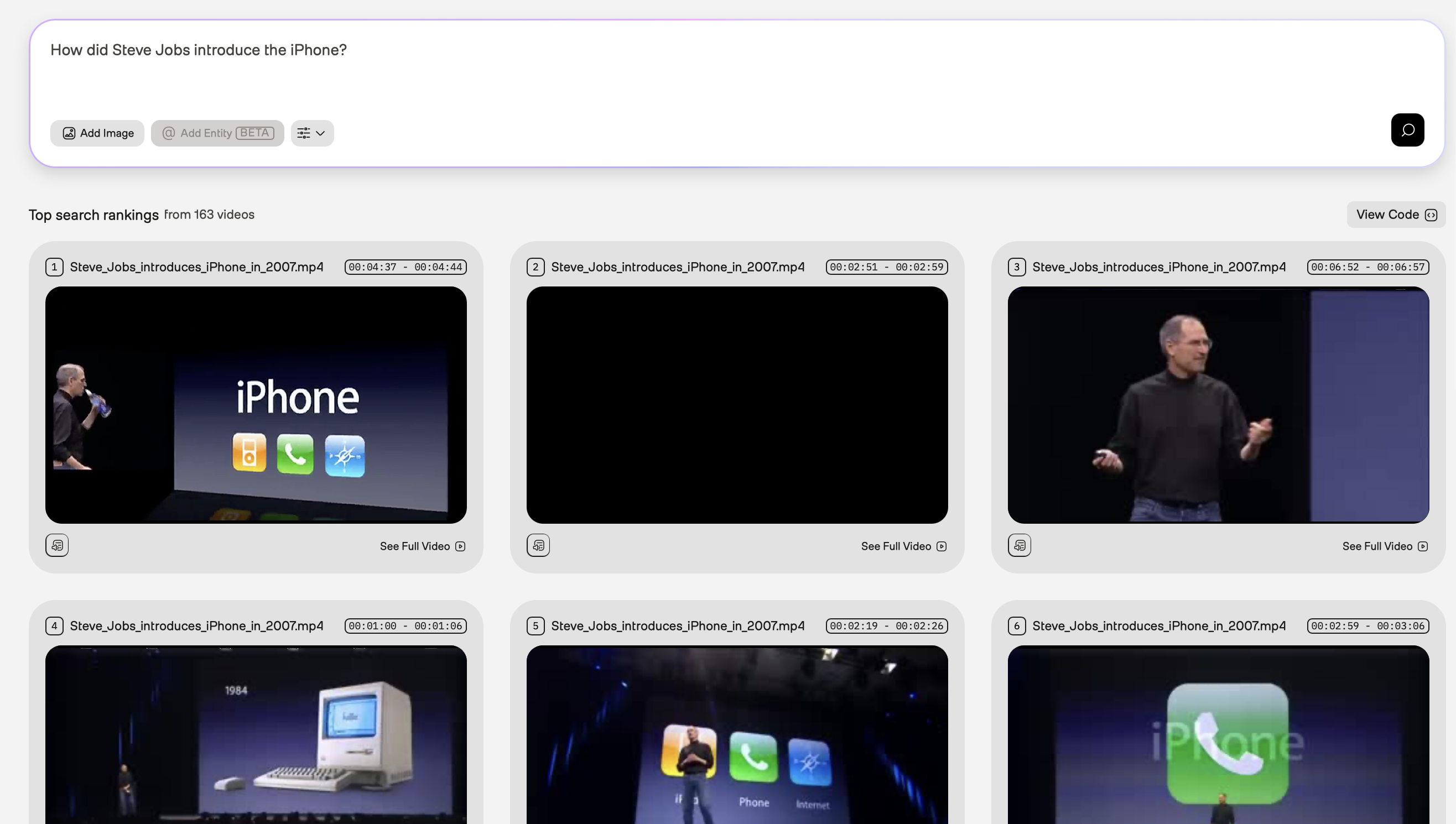
Steve Jobs introducing the iPhone
In the example screenshot below, the query was “How did Steve Jobs introduce the iPhone?”. The Marengo video understanding model used information found in the visual and conversation audio to perform the following tasks:
- Visual recognition of a famous person (Steve Jobs)
- Joint speech and visual recognition to semantically search for the moment when Steve Jobs introduced the iPhone. Note that semantic search finds information based on the intended meaning of the query rather than the literal words you used, meaning that the platform identified the matching video fragments even if Steve Jobs didn’t explicitly say the words in the query.
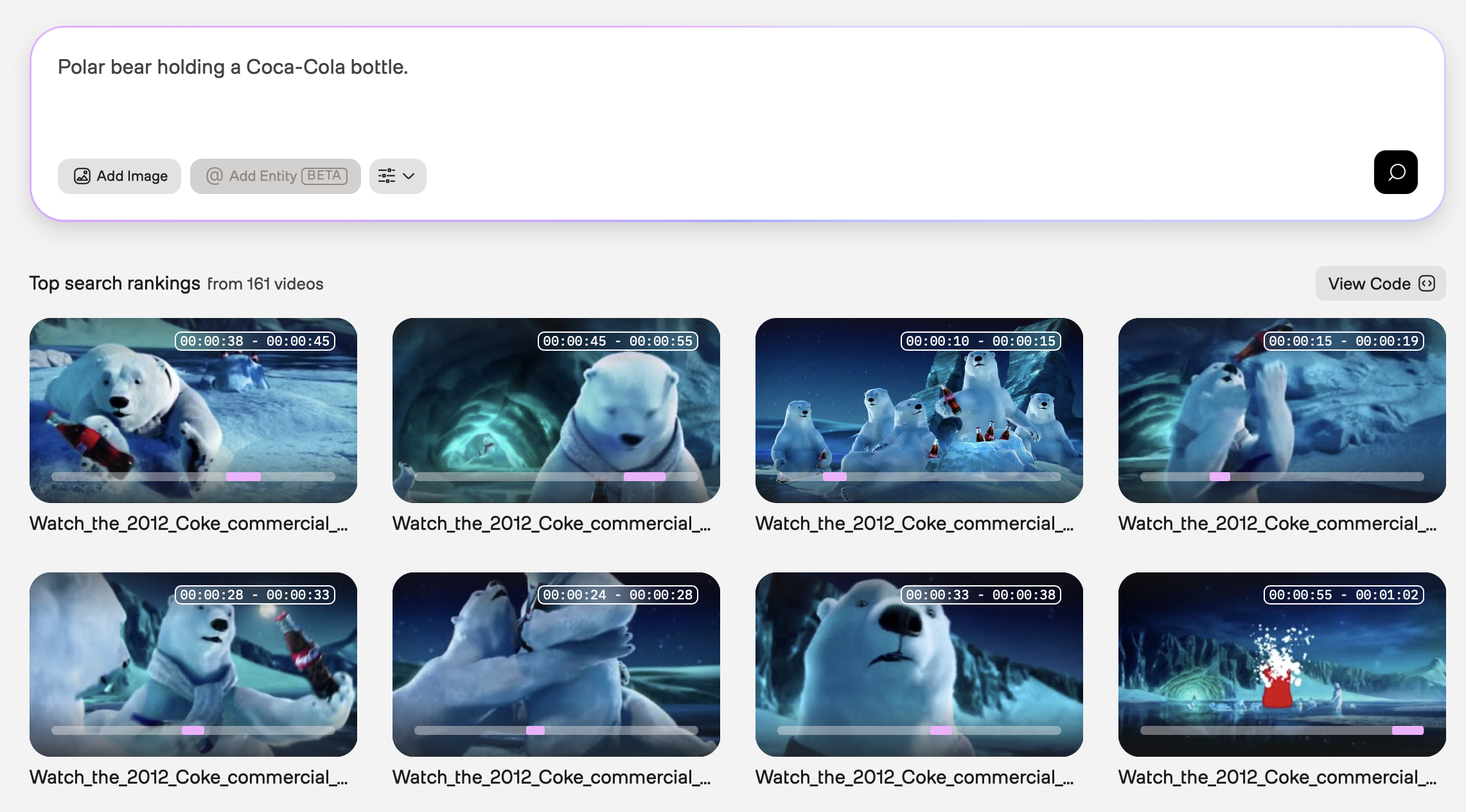
Polar bear holding a Coca-Cola bottle
In the example screenshot below, the query was “Polar bear holding a Coca-Cola bottle.” The Marengo video understanding model used information found in the visual and logo modalities to perform the following tasks:
- Recognition of a cartoon character (polar bear)
- Identification of an object (bottle)
- Detection of a specific brand logo (Coca-Cola)
- Identification of an action (polar bear holding a bottle)
To see this example in the Playground, ensure you’re logged in, and then open this URL in your browser.
Using different languages
This section provides examples of using different languages to perform search requests.
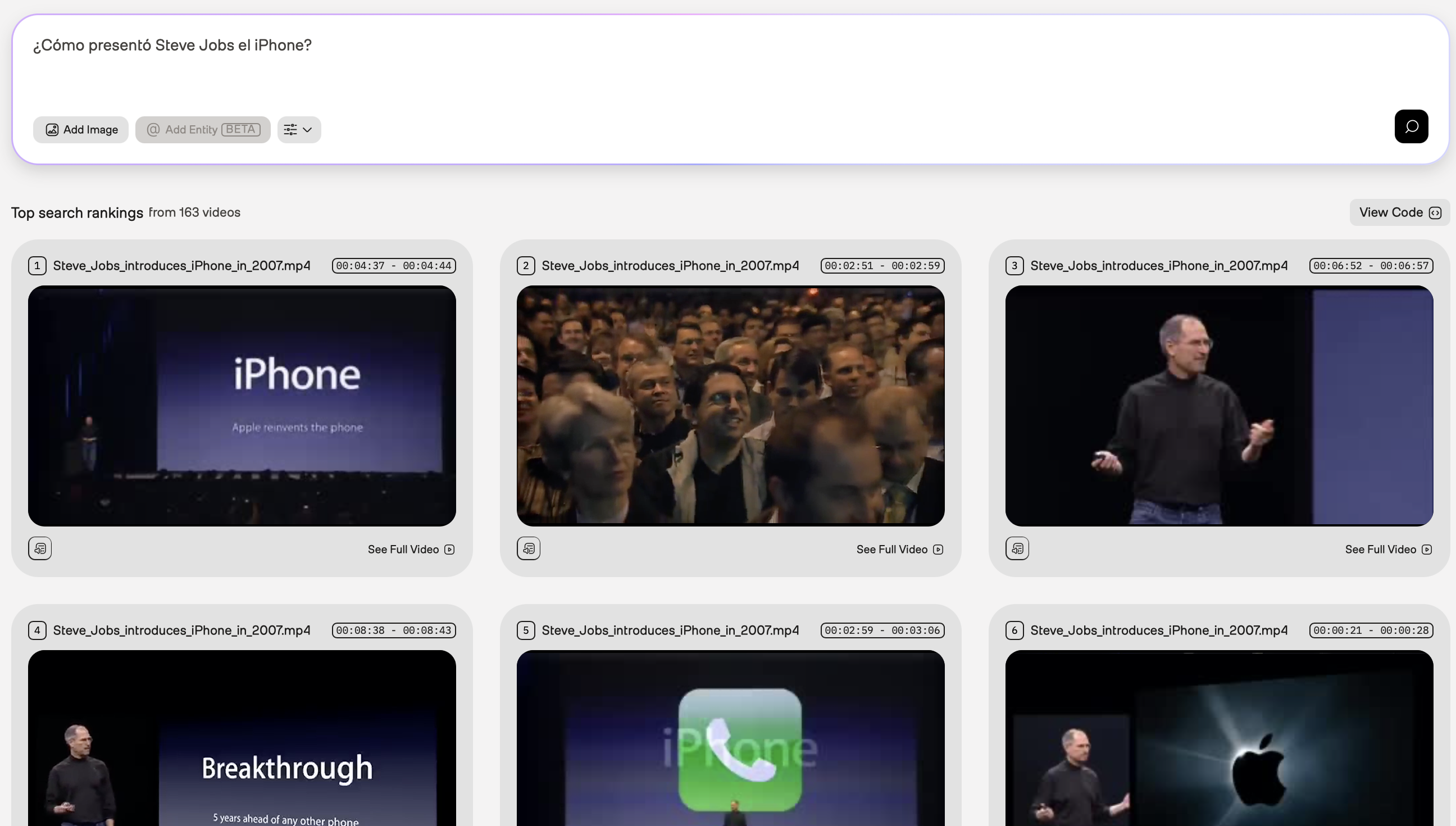
Spanish
In the example screenshot below, the query was “¿Cómo presentó Steve Jobs el iPhone?” (“How did Steve Jobs introduce the iPhone?”). The Marengo video understanding model used information from the visual and audio modalities.
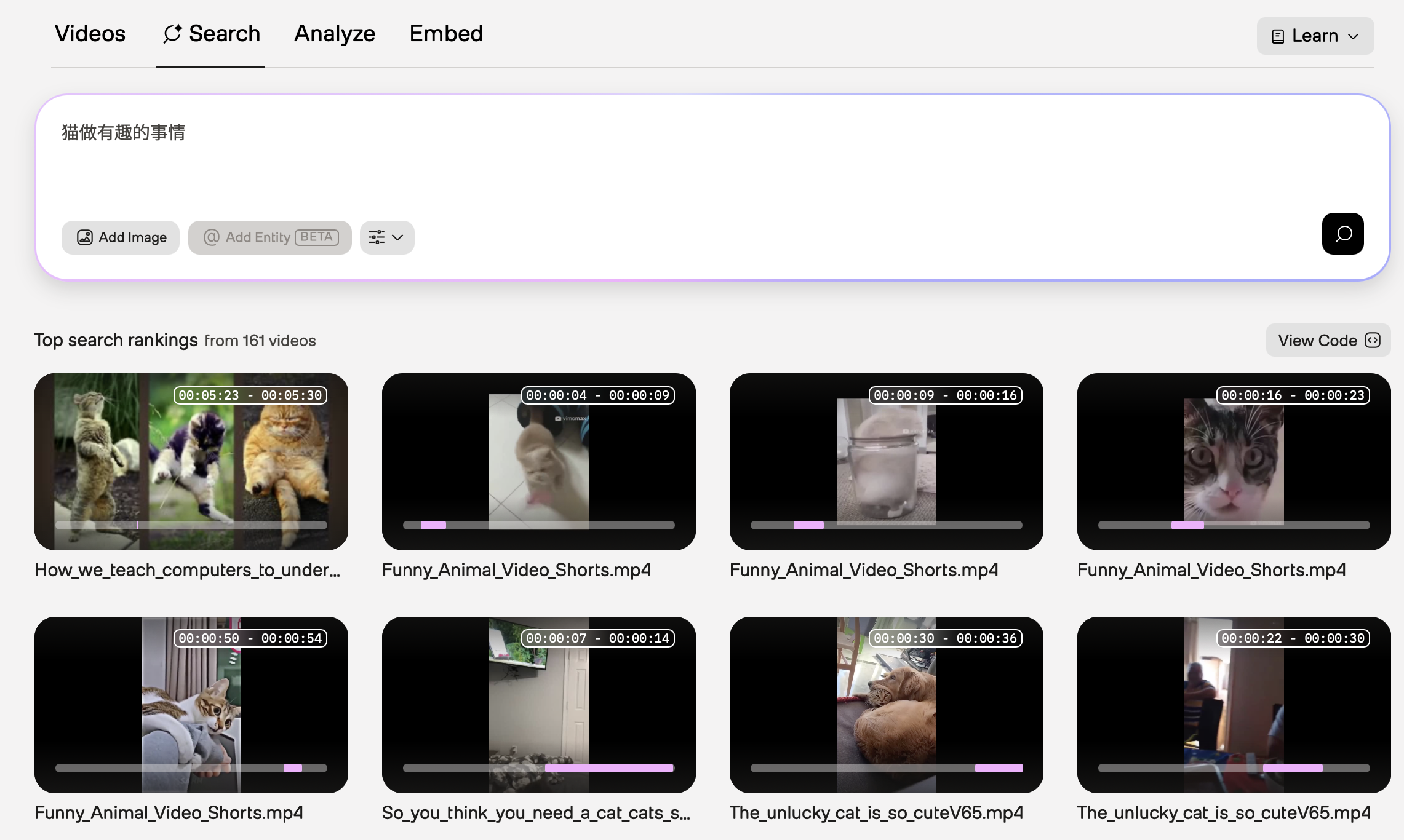
Chinese
In the example screenshot below, the query was “猫做有趣的事情” (“Cats doing funny things.”). The Marengo video understanding model used information from the visual modality.
To see this example in the Playground, ensure you’re logged in, and then open this URL in your browser.
Support
For support or feedback regarding Marengo, contact support@twelvelabs.io.